Gum Grafting
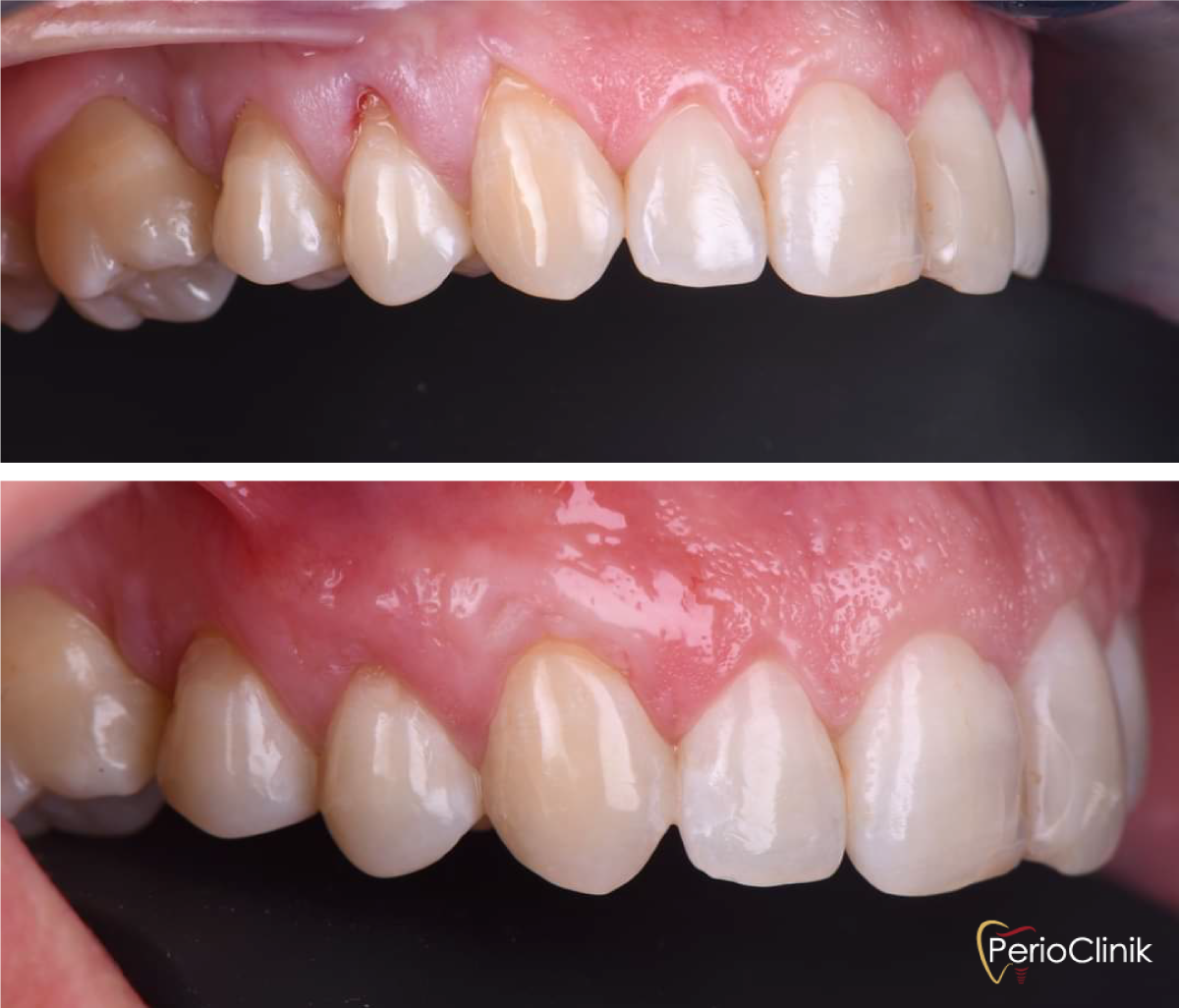
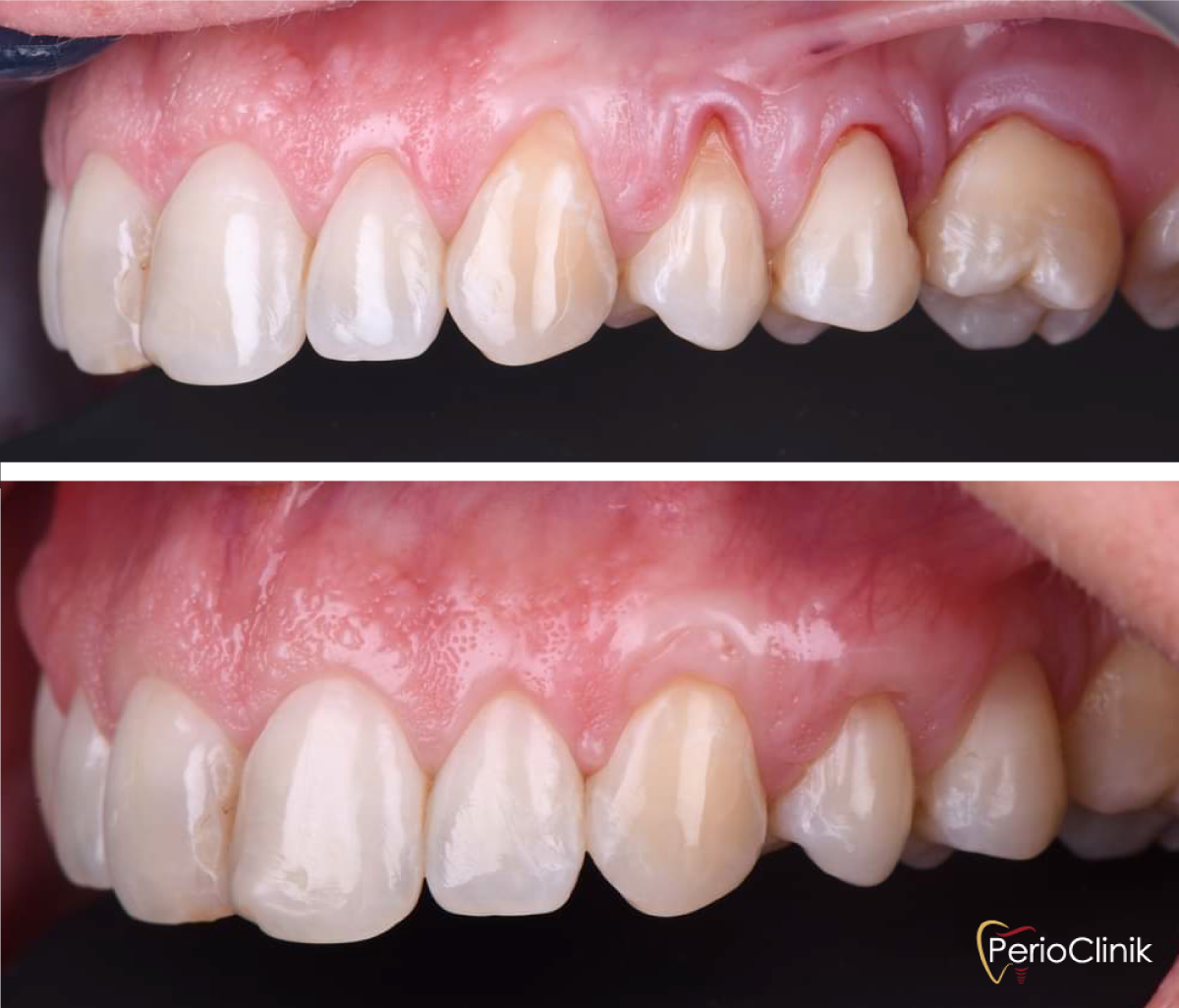
Why Gum Grafting?
Gum recessions causing esthetic issues
Gum recessions causing tooth hypersensitivity or gingival inflammation
Gum recessions showing signs of progression
Inadequate amount of gum around teeth
Types of Gum Graft
Autograft: a gum graft using your own soft tissue, usually sourced from the palate. this is currently the gold standard
Allograft: a gum graft using soft tissue sourced from a human donor
Xenograft: a gum graft using soft tissue from an animal source (bovine or porcine)
Treatment
Free gingival graft, mostly used for soft tissue augmentation
Connective tissue graft, mostly used for root coverage
Case-by-Case Procedure
Sometimes oral or IV sedatives can also be used to achieve a higher state of relaxation depending on the needs of an individual patient. A portion of your own tissue (autograft) is harvested from donor site or manufactured tissue (allograft, xenograft) can be used. A small incision is made at the recipient site. Some soreness may be experienced after the surgery which can be managed by over-the-counter anti-inflammatory medication. Though you will soon feel completely back to normal, it may take your body up to 6 weeks for soft tissue to heal and several months to maturate. The waiting time allows the healing process enough time to achieve the desired aesthetic and functional results.
Local Anesthesia is Applied
Tissue is Harvested from Donor Site

Gum Graft is Positioned & Secured

Tissue Healing




