Ridge Augmentation
Ridge augmentation is a surgical procedure that rebuilds the jawbone in areas where bone has been lost. It’s often performed before dental implant placement to ensure adequate bone height and width for implant stability. This technique improves both function and appearance.
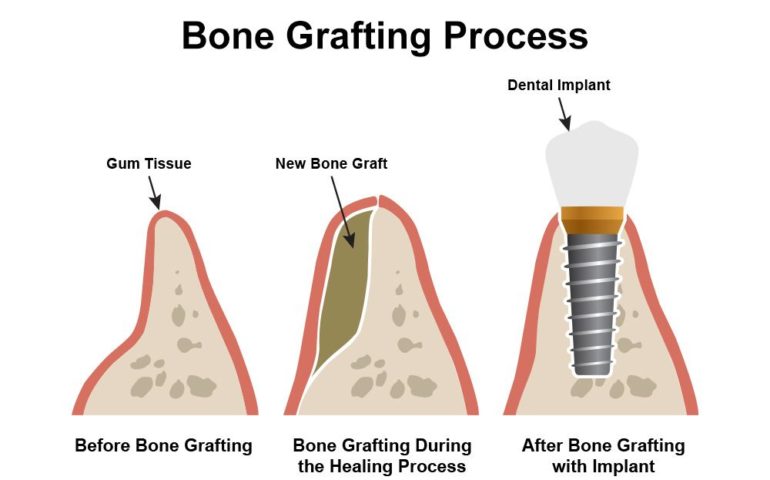
Types of Bone Graft
Autograft: a bone graft using your own bone, usually sourced from the hip bone or back of the jaw.
Allograft: a bone graft using bone sourced from a human donor.
Xenograft: a bone graft using bone from an animal, usually a cow.
Alloplast: a bone graft using synthetic material containing calcium, phosphorous and hydroxylapatite.
Each material is carefully selected based on your medical needs, healing capacity, and implant plan.
Procedure Process
Bone grafting allows the repair of jawbone deficiencies and, in many cases, can be performed at the same time as implant placement and therefore not requiring additional procedures. In some cases, however, a separate procedure is needed based on the severity of the defect. Manufactured material is typically used, thus eliminating the need for harvesting bone from the patient, significantly reducing discomfort and facilitating recovery.
Bone grafting involves 4 key steps, often completed during the same appointment as your dental implant surgery.
01. Local Anesthesia is Applied
02. The Bone Graft is Prepared
03. Bone is deposited
04. Bone Healing
Socket Preservation
Socket preservation prevents bone shrinkage after tooth extraction. It helps maintain ridge volume and improves the outcome of future restorative treatments such as implants or bridges. It’s ideal for patients planning delayed or immediate implant placement.
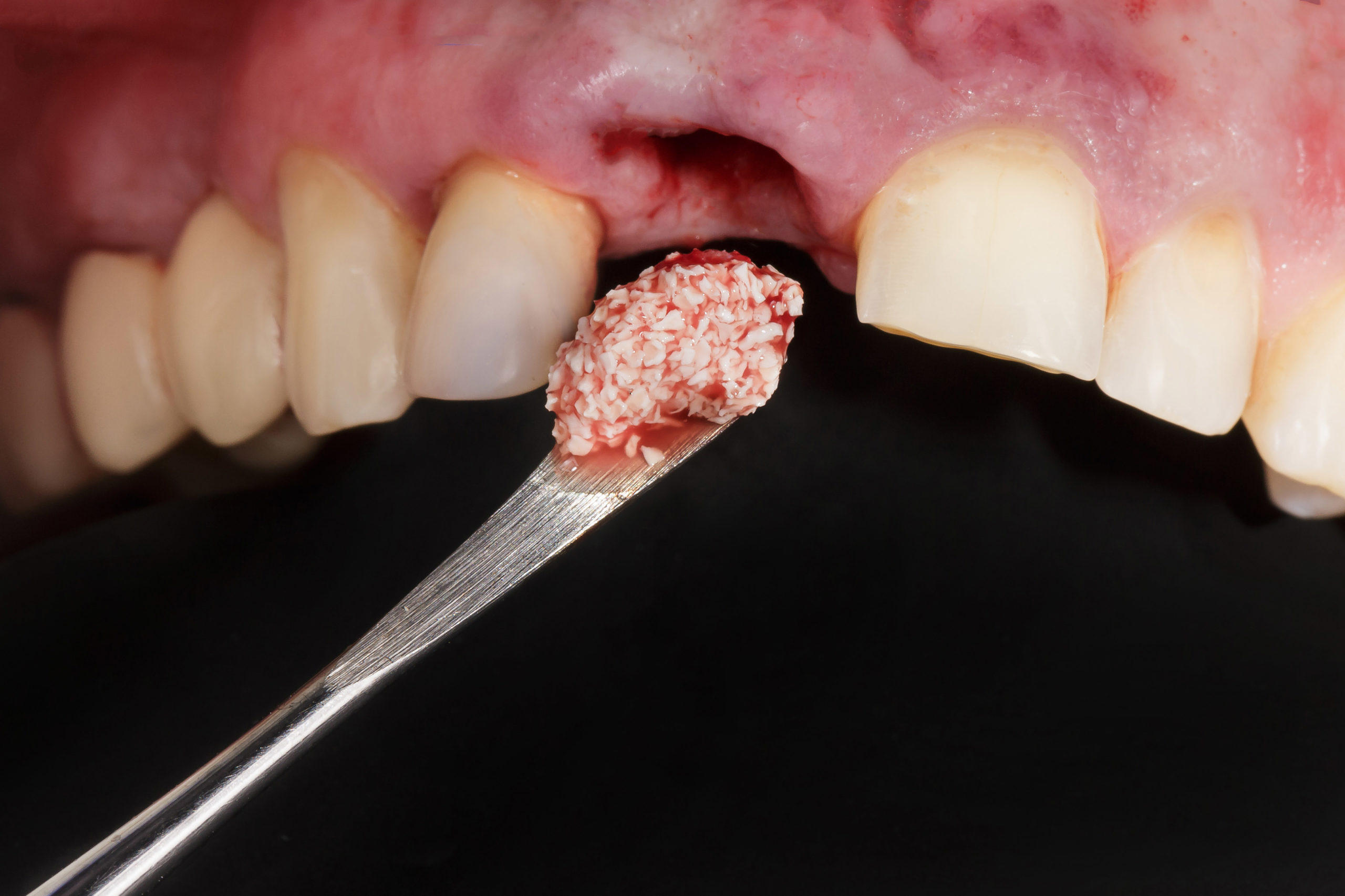
01. Local Anesthesia is Applied
02. Tooth is atraumatically extracted
03. Bone is Deposited in the Socket
04. Bone Healing
Pre & Post Op Instructions
For optimal healing, follow our pre- and post-surgery guidelines. Download detailed forms below for your bone grafting procedure.



